In short: Prehistoric reptiles were among the first animals to live fully on land.
They appeared millions of years before dinosaurs and helped shape life on Earth.
Prehistoric reptiles were among the first animals that could live fully on land without returning to water. These ancient reptiles appeared millions of years before dinosaurs, mammals, cities, or humans. They lived in many environments — crawling through forests, swimming in shallow seas, running on dry land, and even gliding between trees 🌍.
- 📘What Are Prehistoric Reptiles?
- ⏳ When Did Prehistoric Reptiles Live?
- ⭐ Why Are Prehistoric Reptiles Important?
- 📜 Top 15 Prehistoric Reptile Names
- 🆚 Difference Between Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Reptiles
- ❓ FAQs About Prehistoric Reptiles
- 🎉 Fun Facts About Prehistoric Reptiles (For Kids)
- 🧠 Quick Recap Table
- 🧠 Conclusion
In this guide, you will learn what prehistoric reptiles were, when they lived, how they evolved, and why they are important in Earth’s history.
Everything is explained in simple, kid-friendly language.
This guide is best for kids aged 8–12 and parents who enjoy learning together
📘What Are Prehistoric Reptiles?
Prehistoric reptiles were early cold-blooded animals that lived long before dinosaurs.
They were among the first creatures that could live fully on land without returning to water.🦕🦅
These ancient reptiles are different from prehistoric amphibians, and they came before most dinosaurs.
⏳ When Did Prehistoric Reptiles Live?
These time periods help us understand how reptiles slowly changed and evolved over millions of years.
| Time Period | How Long Ago | What Happened |
|---|---|---|
| Carboniferous | ~350 million years ago | First true reptiles appeared |
| Permian | 299–252 million years ago | Giant reptiles evolved |
| Triassic | 252–201 million years ago | Dinosaurs appeared |
🔥 The Permian Mass Extinction
At the end of the Permian Period, Earth experienced the largest mass extinction ever, where about 90% of life disappeared.
Some reptiles survived this disaster — and those survivors later gave rise to dinosaurs, marine reptiles, and mammals.
👉 Some lived alongside prehistoric amphibians — you can learn how reptiles and amphibians differ in this fun guide on Difference Between Amphibians and Reptiles.
⭐ Why Are Prehistoric Reptiles Important?
Learning about Prehistoric Reptiles helps kids understand:
How life evolved on Earth 🧬
Where dinosaurs and mammals came from
Why some animals survived and others disappeared
👉 Prehistoric reptiles lived long before modern reptiles. To learn how today’s reptiles grow from tiny eggs into adults, check out our Reptile Life Cycle guide!
They are an important part of dinosaurs and other prehistoric reptiles history.
📜 Top 15 Prehistoric Reptile Names
Below is a prehistoric reptiles list with fun explanations. Each animal is part of the amazing world of prehistoric reptile animals.
1. 🦎 Hylonomus – The First True Reptile

Name: Hylonomus
Pronunciation: High-LOW-no-muss
🌍 Habitat
Hylonomus lived in dense forest environments with dry land, tall trees, and fallen logs.
It often stayed inside hollow tree trunks, which helped protect it from predators.
⏳ Time Period
This reptile lived during the Late Carboniferous Period, about 315 million years ago, long before dinosaurs existed.
📏 Size
Hylonomus was a very small reptile, about 1 foot long, similar in size to a modern lizard.
Its small body made it quick and agile.
🍖 Diet
It mainly fed on:
- Insects
- Small bugs
- Tiny animals
⭐ Why Hylonomus Is Important
Hylonomus is considered the oldest known true reptile.
It was among the first animals able to lay eggs on land, allowing reptiles to live fully away from water.
🎉 Fun Fact: Hylonomus helped reptiles spread across Earth by living completely on land.
2. 🦎 Araeoscelis – An Early Diapsid Reptile

Name: Araeoscelis
Pronunciation: Ah-RAY-oh-SEE-liss
🌍 Habitat
Araeoscelis lived on dry land in warm environments, where open spaces allowed it to move easily and hunt for food.
⏳ Time Period
It lived during the Early Permian Period, around 290 million years ago.
📏 Size
Araeoscelis was a small and lightweight reptile.
Its long tail helped it stay balanced while running.
🍖 Diet
It likely ate:
- Insects
- Small animals
⭐ Why Araeoscelis Is Important
Araeoscelis was an early diapsid reptile, a group that later gave rise to:
- Dinosaurs
- Birds
- Many modern reptiles
🎉 Fun Fact: Araeoscelis was probably a fast runner for its size.
3. 🦎 Archaeothyris – A Small but Important Reptile
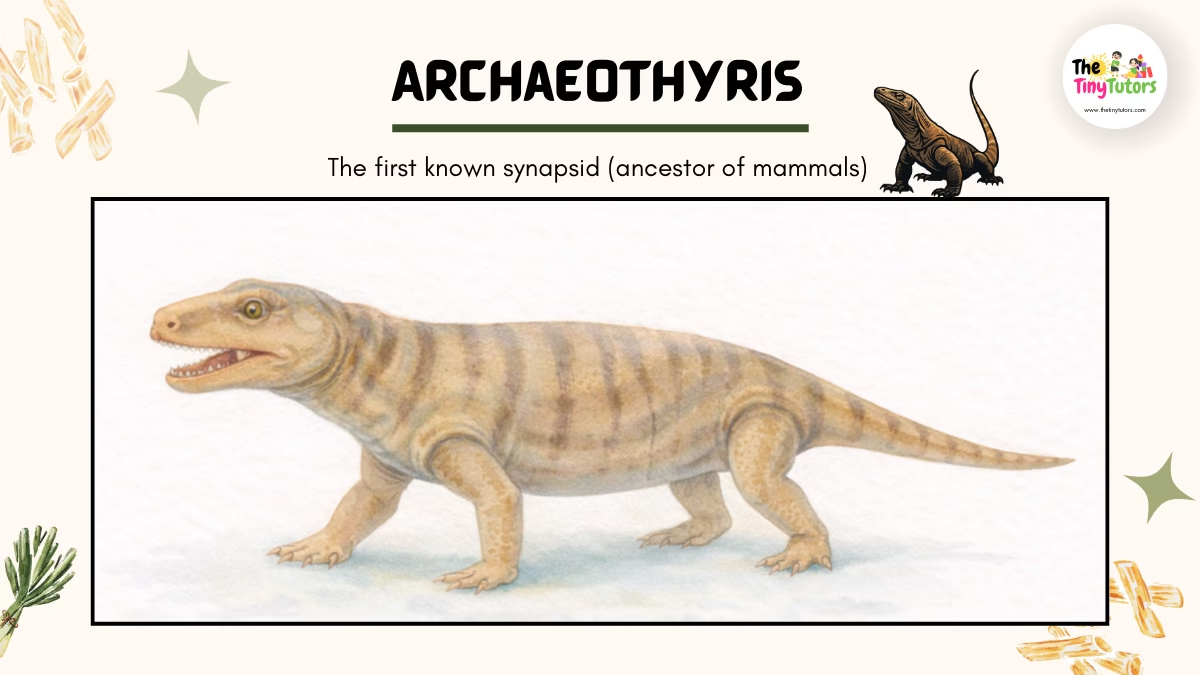
Name: Archaeothyris
👉 Pronunciation: ARE-kay-oh-THIGH-riss
Its name sounds long, but you can remember it by saying it slowly like a rhyme 😊
🌍 Habitat
Archaeothyris lived in warm, swampy environments of ancient North America.
These areas had thick plants, muddy ground, and plenty of insects, which provided both food and hiding places.
⏳ Time Period
This reptile lived during the Late Carboniferous Period, about 305 million years ago, long before dinosaurs appeared on Earth.
📏 Size
Archaeothyris was a small reptile, measuring about 1 to 2 feet in length.
Its lightweight body helped it move quickly and avoid larger predators.
🍖 Diet
It was likely a meat-eater, feeding on:
- Insects
- Small animals
- Tiny amphibians
Sharp teeth and strong jaws made it an effective hunter for its size.
⭐ Why Archaeothyris Is Important
Archaeothyris belongs to a group of early reptiles that later led to mammal-like reptiles.
Over millions of years, this evolutionary line eventually gave rise to early mammals, making Archaeothyris an important part of Earth’s animal history.
🎉 Fun Fact: Even though it was small, Archaeothyris played a big role in the evolution of mammals.
4. 🦎 Bradysaurus – A Large Plant-Eating Reptile
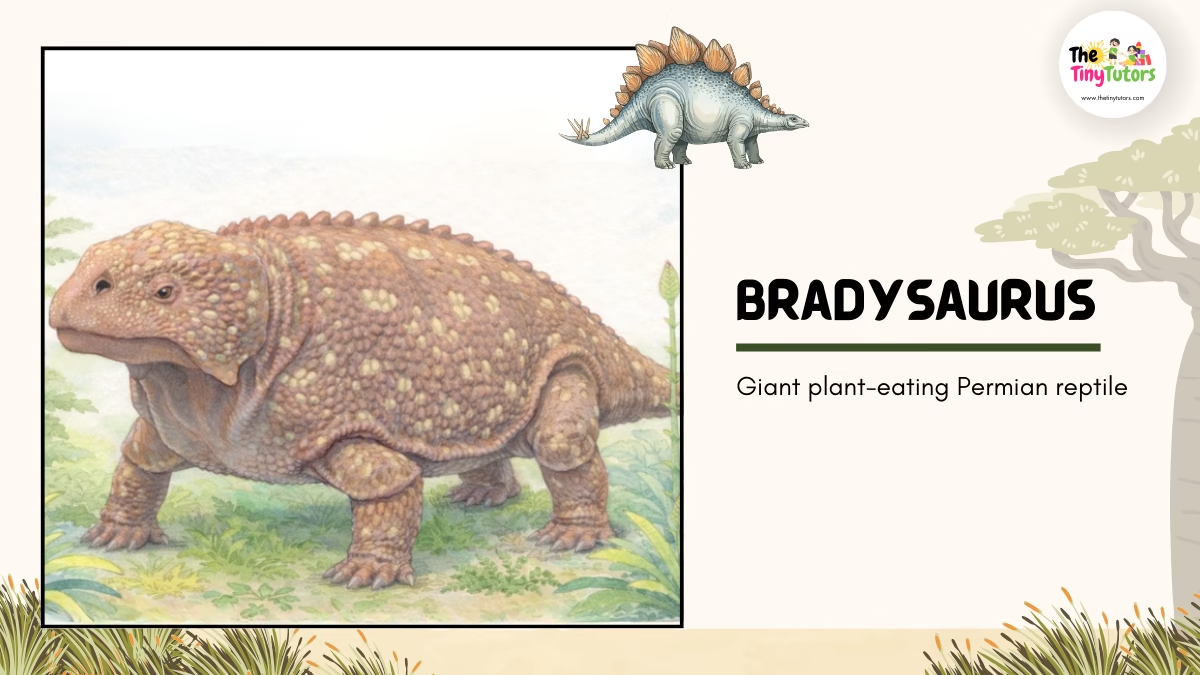
Name: Bradysaurus
Pronunciation: BRAD-ee-SORE-us
🌍 Habitat
Bradysaurus lived on dry land in areas where plants were abundant.
These environments provided enough vegetation to support its large body.
⏳ Time Period
This reptile lived during the Permian Period, about 260 million years ago.
📏 Size
Bradysaurus was a very large and heavy reptile, with a body shape similar to a modern rhinoceros or cow.
Its strong legs supported its thick body.
🌿 Diet
It was a herbivore, feeding mainly on:
- Leaves
- Plants
- Low-growing vegetation
⭐ Why Bradysaurus Is Important
Bradysaurus shows that some prehistoric reptiles grew very large and survived by eating plants rather than hunting other animals.
🎉 Fun Fact: Bradysaurus likely spent most of its time slowly moving and eating plants.
5. 🦎 Coelurosauravus – The Tree Glider

📛 Name: Coelurosauravus
👉 Pronounced as: See-LOOR-oh-SORE-ah-vuss
🌍 Habitat
- Lived in forests 🌳
- Spent lots of time in trees
⏳ Historical Period
- Lived about 260 million years ago
- Late Permian Period
📏 Size
- Small body
- Long ribs
🍖 Diet
- Insects
- Small animals
⭐ Special Ability
- Could glide between trees
- Used skin stretched over ribs
🎉 Fun Fact: It glided like a paper airplane ✈️
6. 🦎 Mesosaurus – The Water Swimmer

📛 Name: Mesosaurus
👉 Pronounced as: MEZ-oh-SORE-us
🌍 Habitat
- Lived in lakes and shallow seas 🌊
- Near land
⏳ Historical Period
- Early Permian Period
- About 280 million years ago
📏 Size
- Medium-sized reptile
- Long body and tail
🍖 Diet
- Fish 🐟
- Water insects
⭐ Special Features
- Flat tail for swimming
- Webbed feet
🎉 Fun Fact: One of the first swimming reptiles!
7. 🦎 Homeosaurus – Ancient Lizard Cousin

📛 Name: Homeosaurus
👉 Pronounced as: HO-me-oh-SORE-us
🌍 Habitat
- Dry land
- Rocky areas
⏳ Historical Period
Late Jurassic Period
📏 Size
- Small and light
- Lizard-like body
🍖 Diet
- Insects
- Small prey
⭐ Importance
- Related to modern tuatara
- Shows how reptiles changed slowly
🎉 Fun Fact: Its relatives still live today in New Zealand 🇳🇿
8. 🦎 Scutosaurus – The Armored Reptile

📛 Name: Scutosaurus
👉 Pronounced as: SKYOO-toh-SORE–us
🌍 Habitat
- Dry land
- Open plains
⏳ Historical Period
Late Permian Period
📏 Size
- Large and heavy
- Thick body armor 🛡️
🌿 Diet
- Plant-eater
- Leaves and plants
⭐ Special Feature
Hard bony plates for protection
🎉 Fun Fact: It was like a walking tank!
9. 🦎 Procolophon – The Survivor
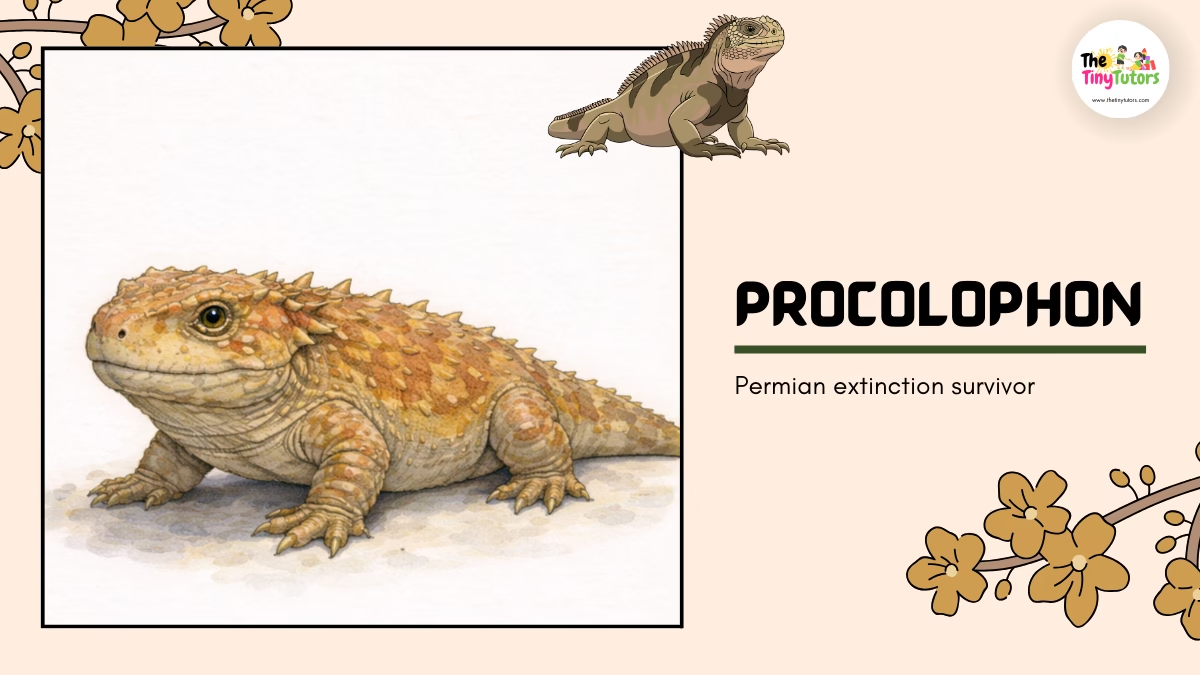
📛 Name: Procolophon
👉 Pronounced as: Pro-KOL-oh-fon
🌍 Habitat
Dry and rocky areas
⏳ Historical Period
- Lived after mass extinction
- Early Triassic Period
📏 Size
Small but strong 💪
🌿 Diet
Plants
Tough food
⭐ Importance
Survived Earth’s biggest extinction
🎉 Fun Fact: Very tough and adaptable!
10. 🦎 Petrolacosaurus – Early Family Tree Member
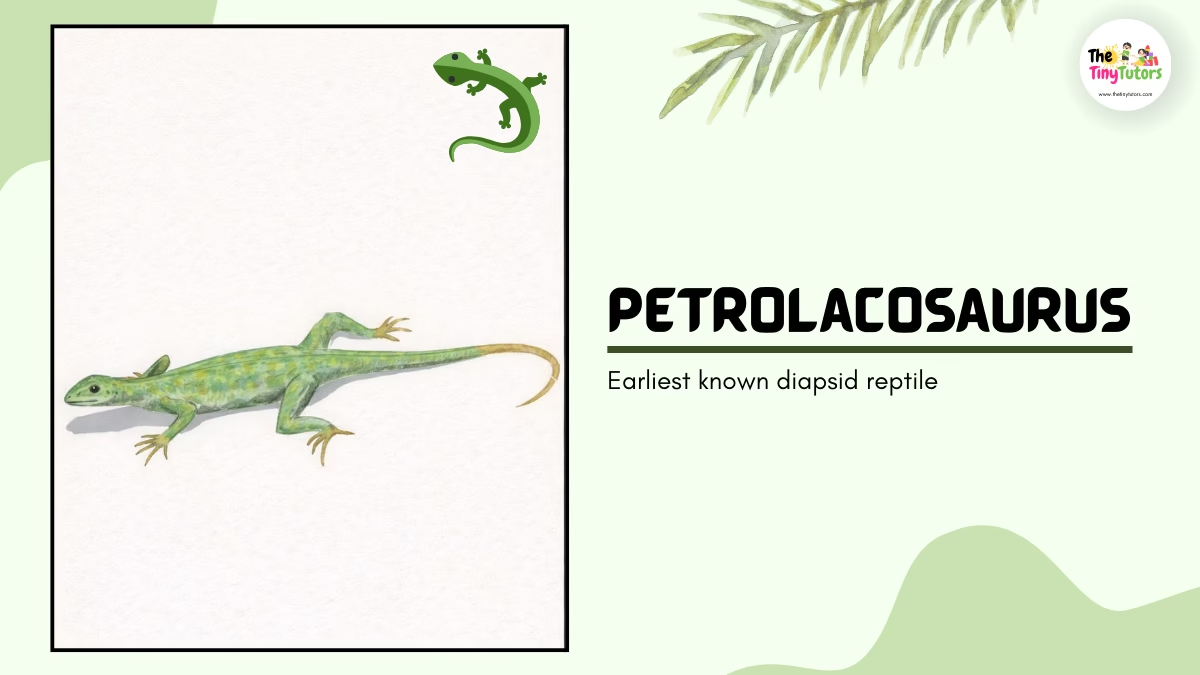
📛 Name: Petrolacosaurus
👉 Pronounced as: PET-ro-LACK-oh-SORE-us
🌍 Habitat
- Forests
- Dry land
⏳ Historical Period
Late Carboniferous Period
📏 Size
Small and fast
🍖 Diet
- Insects
- Small animals
⭐ Importance
- Earliest known diapsid reptile
- Important for reptile evolution
11. 🦎 Icarosaurus – The Gliding Star
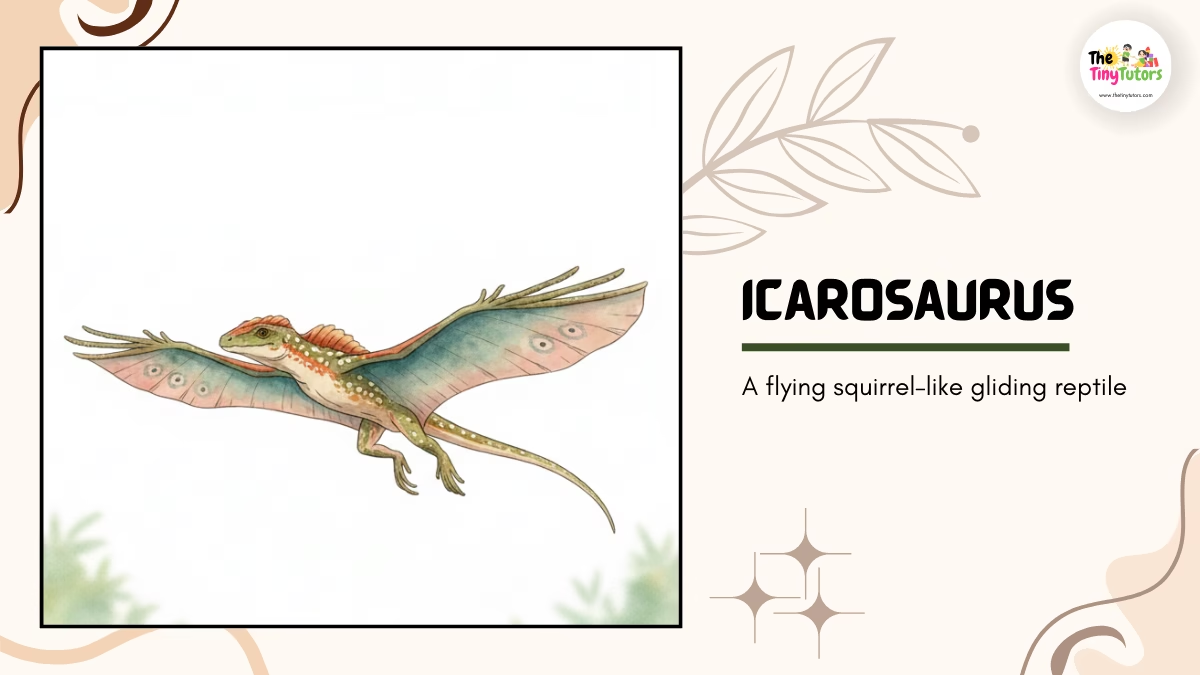
📛 Name: Icarosaurus
👉 Pronounced as: IK-air-oh-SORE-us
🌍 Habitat
- Trees 🌳
- Forests
⏳ Historical Period
Triassic Period
📏 Size
Small and light
🍖 Diet
Insects
⭐ Special Ability
- Glided using skin flaps
- Like a flying squirrel 🐿️
12. 🦎 Kuehneosaurus – Rib-Wing Glider

📛 Name: Kuehneosaurus
👉 Pronounced as: KYOO-nee-oh-SORE-us
🌍 Habitat
Forests
⏳ Historical Period
Triassic Period
📏 Size
Small reptile
🍖 Diet
Insects
⭐ Special Feature
Long ribs helped it glide
13. 🦖 Limnoscelis – Early Meat Eater

📛 Name: Limnoscelis
👉 Pronounced as: LIM-no-SEE-liss
🌍 Habitat
Dry land near water
⏳ Historical Period
Early Permian Period
📏 Size
Large for its time
🍖 Diet
- Meat eater
- Sharp teeth 🦷
⭐ Importance
One of the first large carnivorous reptiles
14. 🔄 Tseajaia – The Transition Reptile
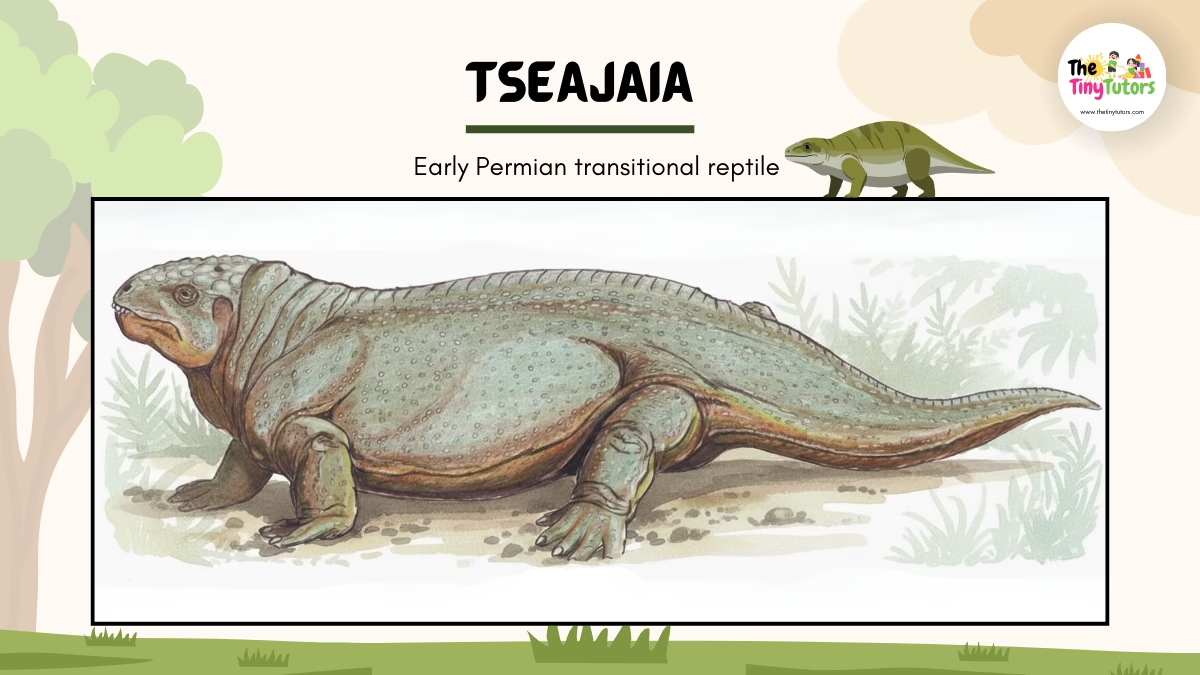
📛 Name: Tseajaia
👉 Pronounced as: Say-AH-jai-uh
🌍 Habitat
Dry land
⏳ Historical Period
Early Permian Period
📏 Size
Medium-sized
🌿 Diet
Plants
⭐ Importance
Link between early reptiles and later ones
15. 🦎 Pareiasaurus – The Giant Plant Eater
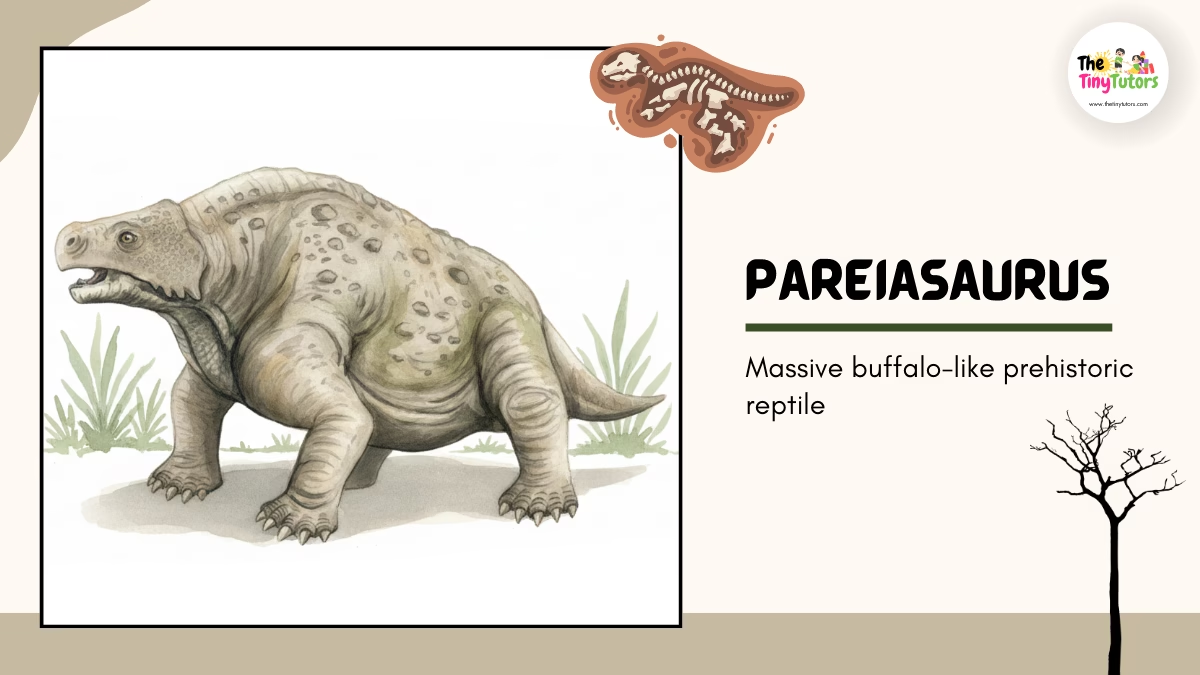
📛 Name: Pareiasaurus
👉 Pronounced as: Pa-RAY-ah-SORE-us
🌍 Habitat
Dry plains
⏳ Historical Period
Late Permian Period
📏 Size
- Very large
- Buffalo-sized 🐃
🌿 Diet
Plants only
⭐ Special Features
- Heavy body
- Slow but powerful
🎉 Fun Fact: It used size, not speed, to stay safe!
🆚 Difference Between Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Reptiles
| Feature | Dinosaurs | Prehistoric Reptiles |
|---|---|---|
| Legs | Under body | Side-spreading |
| Time | Later | Earlier |
| Types | Land only | Land, water, air |
Some prehistoric marine reptiles lived fully in oceans, unlike dinosaurs.
❓ FAQs About Prehistoric Reptiles
Q1: Did all prehistoric reptiles become dinosaurs?
A1: No! Many lived before dinosaurs and went extinct earlier.
Q2: Were they dangerous?
A2: Some were, but many were peaceful plant-eaters 🌿
Q3: Did any live in water?
A3: Yes! Mesosaurus is a great example.
🎉 Fun Facts About Prehistoric Reptiles (For Kids)
- Some reptiles survived giant volcanoes 🌋
- Others glided without wings
- Many lived before dinosaurs
- Some fossils are older than mountains!
🧠 Quick Recap Table
| Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Flying | Icarosaurus |
| Swimming | Mesosaurus |
| Armored | Scutosaurus |
| Plant-Eater | Pareiasaurus |
🧠 Conclusion
Prehistoric Reptiles teach us how life changed over millions of years. From tiny forest climbers to giant armored animals, these ancient reptiles help kids explore Earth’s amazing past in a fun and educational way. 🌍🦎
👉 Now you know about ancient reptiles — Explore more fun guides like Biggest vs Smallest Reptiles and Reptile Adaptations!

